How to Lose Weight Fast: Tips for Permanent Weight Loss
If you want to learn how to lose weight, I honestly believe this article is the best free guide on the internet.
As a professional athlete with an M.S. in Nutrition Education, I believe I have a complex knowledge of how to promote weight loss and body composition improvements that others just don’t have.
I hope you find this article as helpful as I intended because I truly believe I have created an outstanding resource for you!
No matter the reason behind your desire to lose weight fast, it’s important to approach your goals with a healthy mindset and informed strategies.
Although fad diets or extreme exercise routines that offer rapid weight loss can be enticing, these approaches are dangerous and unsustainable.
Instead of falling into one of those traps, this article provides scientifically-backed strategies that are safe, effective, and sustainable strategies.
Also, we’ll explore the role of macronutrients in calorie intake, so you can make informed decisions about what to eat and how much to consume.
Additionally, we will dive into the importance of exercise, how it can support your weight loss and fat-burning goals, and the crucial role of sleep in regulating your metabolism and promoting overall health and wellness.
But that’s not all – we’ll also explore some lesser-known strategies for weight loss and fat burning, such as the role of gut health and the importance of stress management.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a comprehensive understanding of how to lose weight fast in a way that works for your needs and lifestyle.
What is the Difference Between Losing Weight and Burning Fast?
The difference between losing weight and burning fat is subtle but critically important—especially if your goal is improving body composition and overall health.
Losing Weight
Losing weight refers to a reduction in overall body mass, which includes not just fat, but also water, muscle tissue, glycogen, and even bone density in extreme cases.
For example, when people start a crash diet or extreme calorie restriction, they often lose a lot of weight quickly—most of which is water weight and lean muscle, not actual body fat.
That kind of loss can lower the number on the scale, but it doesn’t necessarily mean your body is healthier or more metabolically efficient.
Burning Fat
Fat burning, on the other hand, is the process of using stored adipose tissue (body fat) as fuel—often during moderate-intensity activity, caloric restriction, or after glycogen stores are depleted.
This is a more targeted and desirable outcome because it improves your body composition by reducing fat while maintaining or increasing lean muscle mass.
When people say they want to “tone up” or “get leaner,” they’re really talking about burning fat—not just losing weight.
Why the Distinction Matters
- Weight loss without fat loss can result in a slower metabolism, reduced strength, and a higher chance of regaining weight later.
- Fat loss with muscle retention or gain leads to better insulin sensitivity, improved metabolic rate, and long-term weight management.
Sustainable weight loss usually comes from a modest calorie deficit, strength training, adequate protein intake, and smart cardio—not from crash diets or endless hours of high-intensity exercise.
Can You Lose Weight Without Exercise?
Yes, you can lose weight without exercise, but there are important nuances to understand.
Weight loss fundamentally comes down to the calorie balance equation:
If you consume fewer calories than your body uses (a calorie deficit), you will lose weight—even without physical activity.
In fact, studies consistently show that diet has a greater impact on weight loss than exercise alone.
It’s entirely possible to reduce body weight by adjusting food intake through portion control, reducing calorie-dense foods, and focusing on nutrient-rich meals (Hall et al., 2011).
Downsides of Not Exercising When Losing Weight
However, you will probably lose more muscle!
When weight is lost through diet alone, you’re more likely to lose a combination of:
- Body fat
- Muscle mass
- Water weight
This is important because losing muscle slows your metabolism, making it easier to regain fat later.
Exercise—especially resistance training—helps preserve or build muscle during weight loss, which is essential for long-term results and body composition.
Even if weight is dropping, not exercising can result in:
- Weaker cardiovascular health
- Reduced metabolic flexibility
- Poorer mood and mental health
- Increased risk of weight regain
So, yes, you can lose weight without exercise, but it’s far more effective—and sustainable—to combine a smart dietary strategy with physical activity.
Even simple activities like walking or bodyweight exercises can help maintain muscle mass, support metabolic health, and prevent rebound weight gain.
For long-term success, prioritize high-protein meals, whole foods, and fiber, and aim to move your body daily, even if it’s not formal exercise.
How to Lose Weight Fast Naturally & Permanently
If you’re ready to say goodbye to crash diets and unsustainable exercise routines and hello to a healthy, sustainable, and enjoyable approach to weight loss and fat burning, let’s dive in and discover how you can achieve your goals in a safe, sustainable, and enjoyable way!
Step 1: Set a Clear Goal
Setting a clear and measurable goal is the foundation of a successful weight loss journey.
Without a defined target, it’s challenging to stay motivated or track progress effectively.
A clear goal provides direction and purpose, helping you make consistent choices aligned with your desired outcomes.
Determining Your Weight or Body Fat Goals
Start by assessing your current weight and body composition to set a baseline.
Tools like the Bodypedia Smart Scale can measure not only your weight but also metrics such as body fat percentage, muscle mass, and water weight.
These additional insights allow you to focus on improving body composition—not just dropping pounds—so your efforts lead to fat loss while preserving lean muscle.
To determine how much weight or body fat you want to lose:
- Calculate Your Ideal Weight: Use tools like the Body Mass Index (BMI) as a general guideline, but also consider factors like muscle mass and overall health. Aim for a range rather than a specific number to allow flexibility.
- Set a Realistic Fat Loss Target: Aiming to lose 1–2 pounds of weight or 0.5–1% body fat per week is considered safe and sustainable. For example, if your goal is to reduce 10% body fat, plan for at least 10–20 weeks of consistent effort.
Using SMART Goals for Weight Loss

Using the SMART Goals framework ensures that your weight loss targets are practical and achievable:
- Specific: Define exactly what you want to achieve. For instance, instead of saying, “I want to lose weight,” specify, “I want to lose 10 pounds and reduce my body fat percentage by 5%.”
- Measurable: Use quantifiable metrics like pounds, inches, or body fat percentage to track progress. Smart scales, body measurements, or progress photos are excellent tools for this.
- Achievable: Be honest about what is feasible given your current lifestyle. For example, losing 50 pounds in two months is unrealistic and can be harmful, but 10–15 pounds over three months is both safe and attainable.
- Relevant: Ensure your goal aligns with your broader health and wellness objectives. Ask yourself why this goal matters and how achieving it will improve your quality of life.
- Time-Bound: Set a deadline to create a sense of urgency and focus. For example, “I will lose 10 pounds in 12 weeks by following a structured meal plan and exercising three times per week.”
Breaking Down Your Goal
Divide your overarching goal into smaller, manageable milestones. For instance:
- Lose 3 pounds in the first month.
- Reduce 1% body fat within the first six weeks.
- Increase daily step count by 2,000 steps over the next month.
By focusing on incremental progress, you’ll maintain motivation and create a roadmap for long-term success.
Stay Accountable
Document your goal and share it with a trusted friend, family member, or coach.
Regularly reviewing your progress and adjusting your plan when necessary will keep you on track.
Remember, setting a clear goal is not just about what you want to achieve but also about designing a sustainable strategy to get there.
Step 2: Understanding Weight Loss
As I explained before, weight loss and fat burning are often used interchangeably, but they refer to different concepts.
Weight loss refers to the reduction in overall body weight, including water, muscle, and fat loss, while fat burning refers to the process of using stored body fat as fuel for energy.
Losing weight may not necessarily mean burning fat, as you may lose muscle and water weight instead.
However, our goal is to lose weight and burn as much fat as possible, so the weight loss is permanent.
The Energy Balance Equation
To lose weight fast, you need to create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories than you burn, which can be achieved by reducing your calorie intake through diet and increasing your calorie expenditure through exercise.
The energy balance equation is a concept that refers to the balance between the calories consumed and the calories expended by an individual. re
This equation is the fundamental principle of weight management, and it states that for an individual to maintain their current weight, the number of calories consumed must be equal to the number of calories expended.
In contrast, if an individual consumes more calories than they expend, they will gain weight, while if they expend more calories than they consume, they will lose weight.
To achieve weight loss, an individual must create a calorie deficit, meaning they must consume fewer calories than they expend.
This can be achieved through a combination of diet and exercise.
Consuming fewer calories through a balanced and nutritious diet can reduce the “calories in” component of the energy balance equation.
Increasing the number of calories expended through exercise, NEAT, BMR, and RMR can reduce the “calories out” component of the equation.
For example, an individual who reduces their calorie intake by 500 calories per day and burns an additional 500 calories per day through exercise can achieve a calorie deficit of 1000 calories per day.
This deficit can lead to a weight loss of approximately 1-2 pounds per week.
The energy balance equation is a fundamental principle of weight management, and it states that for an individual to maintain their current weight, the number of calories consumed must equal the number of calories expended.
To achieve weight loss, an individual must create a calorie deficit by consuming fewer calories and increasing the number of calories expended through exercise, NEAT, BMR, and RMR.
By understanding and applying the energy balance equation, individuals can effectively manage their weight and improve their overall health.
Calories In – Does Calorie Source Matter?
Calorie intake by macronutrient source refers to the number of calories an individual consumes from carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Each macronutrient source contains a different number of calories per gram.
Carbohydrates and proteins contain 4 calories per gram, while fats contain 9 calories per gram.
Not all calories are equal, and calories from certain sources can have different effects than others.
The concept of “a calorie is a calorie” suggests that all calories are created equal, regardless of the calorie source.
In other words, a calorie from a piece of cake is the same as a calorie from a serving of vegetables.
This concept suggests that as long as an individual is in a calorie deficit, meaning they are burning more calories than they are consuming, they will lose weight regardless of the source of those calories.
However, this concept is oversimplified and, ultimately, wrong.
While it is true that being in a calorie deficit is necessary for weight loss, not all calories are created equal.
Different sources of calories have different effects on the body, including their impact on metabolism, satiety, and nutrient absorption.
For example, a calorie from a serving of vegetables will have a different effect on the body than a calorie from a piece of cake.
Satiety
Vegetables are nutrient-dense and high in fiber, which can increase satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
Satiety refers to the feeling of fullness and satisfaction after a meal.
Consuming a diet high in protein and fiber has been shown to increase satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
Protein and fiber take longer to digest, which can help an individual feel full for longer periods, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
In contrast, a piece of cake is typically high in sugar and refined carbohydrates, which can lead to a spike in blood sugar and insulin levels, promoting fat storage and increased hunger and cravings.
Thermic Effect of Food
Furthermore, the source of the calorie can impact metabolism.
Protein, for example, has a higher thermic effect of food, meaning it requires more calories to digest and metabolize than carbohydrates and fats, which can ultimately lead to a higher calorie burn during digestion, supporting weight loss and fat-burning goals.
The thermic effect of food refers to the number of calories required to digest, absorb, and metabolize the nutrients from food.
This process requires energy, and the thermic effect of food can vary between different macronutrient sources.
Protein has the highest thermic effect of food, requiring up to 30% of the total calories consumed to digest and metabolize.
Carbohydrates and fats have a lower thermic effect of food, requiring 5-10% and 0-3% of the total calories consumed, respectively.
Overall, the concept of “a calorie is a calorie” is too simplistic and doesn’t consider the impact of different sources of calories on metabolism, satiety, and nutrient absorption.
It’s important to focus on consuming nutrient-dense, whole foods that support overall health and wellness while also being mindful of calorie intake to support weight loss and fat-burning goals.
Understanding the calorie intake by macronutrient source, satiety, and the thermic effect of food can help individuals make informed dietary choices.
For example, consuming a diet high in protein and fiber can increase satiety and reduce overall calorie intake while also increasing the thermic effect of food, resulting in a higher calorie burn during digestion.
This can ultimately support healthy weight loss and management.
Calories Out
Calories out refers to the number of calories that an individual expends through various metabolic processes, including the thermic effect of food, non-exercise physical activity thermogenesis (NEAT), exercise, basal metabolic rate (BMR), and resting metabolic rate (RMR).
As mentioned above, the thermic effect of food is the energy required to digest, absorb, and metabolize the nutrients from food.
This process requires energy and can account for up to 10% of the total energy expenditure.
NEAT is the energy expended during non-exercise activities, such as fidgeting, standing, and walking.
NEAT can vary greatly between individuals and can account for up to 50% of the total energy expenditure.
Exercise refers to targeted physical activity that an individual engages in, such as running, weightlifting, or biking.
Exercise is a prominent way to increase the number of calories expended and can lead to weight loss.
BMR is the number of calories that an individual burns while at rest.
This includes the energy required to maintain vital functions such as breathing, circulation, and organ function.
RMR is similar to BMR but also includes the energy required for light activities such as walking around the house or office.
RMR can account for up to 70% of the total energy expenditure.
How Much Weight Should You Lose Per Week?
The amount of weight an individual should aim to lose per week depends on various factors, including their starting weight, body composition, and overall health status.
In general, a safe and sustainable weight loss rate is 1-2 pounds per week because losing weight too quickly can lead to metabolic adaptations and other health problems.
Metabolic adaptation to weight loss refers to the process by which the body adjusts its metabolism in response to energy intake and expenditure changes, particularly during weight loss.
When an individual reduces caloric intake to lose weight, their body will begin to burn stored fat for energy.
However, as the body loses weight, it may also adapt by reducing its metabolic rate to conserve energy.
This can make it more difficult to continue losing weight as the body’s energy needs decrease.
Additionally, metabolic adaptations can lead to weight regain if an individual returns to their previous eating habits.
Therefore, aiming for a slow and steady weight loss of 1-2 pounds per week is recommended.
This allows the body to gradually adapt to the changes in energy intake and expenditure, reducing the risk of metabolic adaptation and increasing the likelihood of long-term weight loss success.
Attempting to lose weight too quickly can lead to drastic calorie deficits, triggering metabolic adaptations and undesirable consequences, such as muscle loss, fatigue, and slowed metabolism.
Additionally, rapid weight loss can be unsustainable and difficult to maintain long-term, increasing the likelihood of weight regain.
Furthermore, rapid weight loss often involves unsustainable or unhealthy methods, such as extreme calorie restriction or excessive exercise, which can be harmful in the long term.
Weight loss should always be approached in a personalized and gradual manner, focusing on making sustainable lifestyle changes rather than quick fixes.
Step 3: Establish a Weight Loss Diet Plan
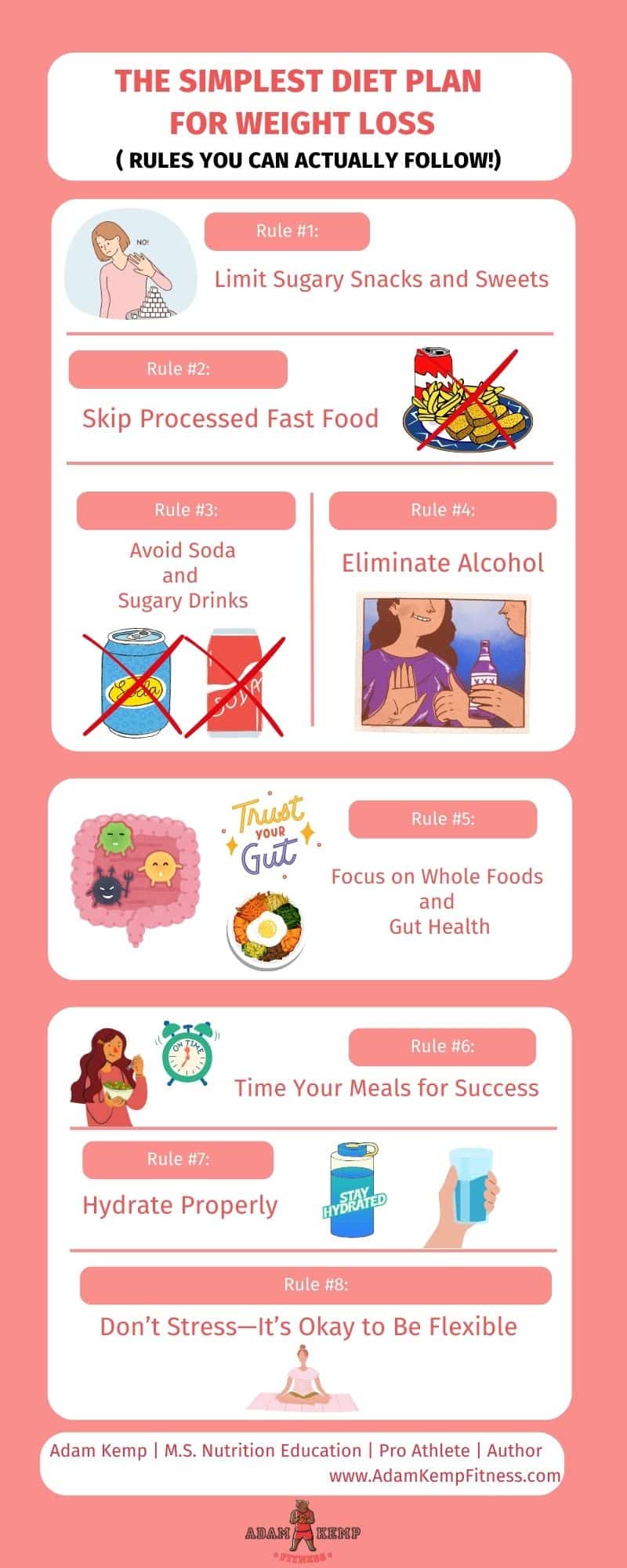
A simple weight loss diet plan plays a crucial role in your success with losing weight and burning fat.
A balanced diet that provides all the necessary nutrients while limiting calorie intake is essential for optimal health, and a diet high in protein, fiber, and healthy fats can help reduce hunger and increase satiety, leading to reduced calorie intake.
Protein
Protein is a crucial macronutrient that plays an important role in weight loss and fat-burning goals.
One of the primary ways protein supports weight loss is through its impact on satiety.
Consuming protein-rich foods can help an individual feel fuller for longer, reducing the likelihood of overeating and promoting a calorie deficit.
Protein plays a role in regulating hunger hormones, such as leptin and ghrelin.
Leptin is a hormone that signals feelings of fullness and satiety to the brain, while ghrelin is responsible for stimulating hunger.
Consuming a diet high in protein has been shown to increase leptin levels and decrease ghrelin levels, ultimately reducing hunger and increasing satiety.
In one study, individuals who consumed a high-protein breakfast reported feeling more full and satisfied throughout the day and consumed fewer calories at subsequent meals.
This suggests that consuming protein-rich foods early in the day can help promote satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
In addition, protein has a higher thermic effect of food compared to carbohydrates and fats, meaning that it requires more calories to digest and metabolize.
This ultimately leads to a higher calorie burn during digestion, supporting weight loss goals.
Another way protein supports weight loss is through its role in muscle growth and maintenance.
Consuming adequate amounts of protein is essential for preserving lean muscle mass while losing body fat, which is important because muscle is metabolically active tissue that burns calories even at rest.
The more muscle an individual has, the more calories they will burn throughout the day, even during periods of inactivity.
This makes protein a valuable nutrient for individuals looking to maintain or increase their metabolism while losing weight.
Animal vs. Plant Protein for Weight Loss
Both animal and plant proteins can be beneficial for weight loss, as they can help increase satiety, support muscle growth and maintenance, and contribute to a balanced diet.
However, there are some differences between the two.
Animal proteins, such as those found in meat, fish, and dairy, are considered “complete” proteins because they contain all the essential amino acids the body requires.
Animal proteins are also generally higher in leucine, an amino acid that is particularly important for muscle protein synthesis.
Plant proteins, such as those found in beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds, are often considered “incomplete” because they may lack one or more essential amino acids.
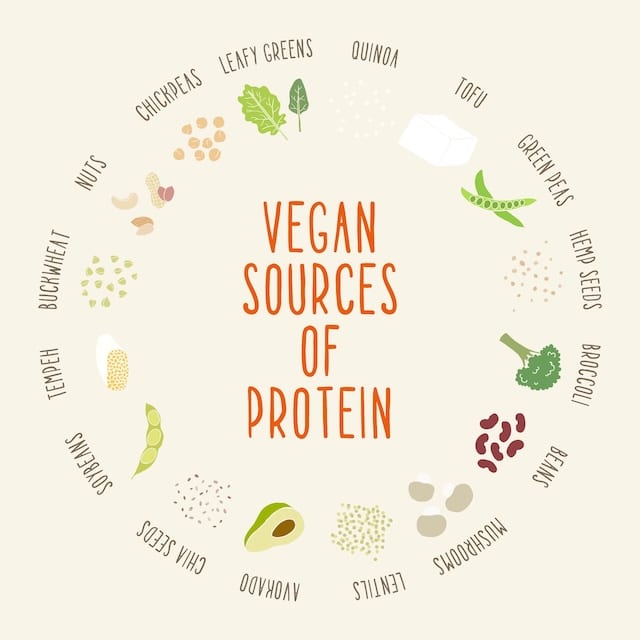
However, consuming various plant protein sources can help ensure that all essential amino acids are obtained.
Plant proteins are also generally lower in fat and calories than animal proteins.
Additionally, plant proteins like beans and lentils are very affordable, making them one of the best protein sources if you are trying to lose weight on a budget.
In terms of weight loss, both animal and plant proteins can be effective.
However, some studies have suggested that plant-based diets may be more effective for weight loss and weight management.
This may be partly due to the higher fiber content of many plant-based protein sources, which can increase satiety and reduce overall calorie intake.
Ultimately, the best source of protein for weight loss may depend on individual preferences and dietary restrictions.
Both animal and plant proteins can play a role in a healthy, balanced diet that supports weight loss and management.
Carbohydrates
Although there is tons of marketing aimed at low-carbohydrate diets for weight loss, carbohydrates are incredibly important in promoting overall health and healthy, long-term weight loss.
You may not be familiar with this phrase, but “fats burn in a flame of carbohydrates.”
This phrase refers to the body’s reliance on carbohydrates as a primary energy source to fuel fat-burning processes.
Without going too deep into the science, after carbohydrates are consumed, they are converted into glucose, which is then used by the body as a primary source of fuel.
This process occurs in the presence of oxygen, which is why it is also known as aerobic metabolism.
The body requires a sufficient supply of glucose to lose weight efficiently.
If glucose levels are low, the body may not be able to access stored fat for energy.
This can make it difficult to lose weight, as the body will be forced to rely on alternative energy sources, such as muscle protein, which can lead to muscle wasting and a decrease in overall metabolism, making it even harder to lose weight and burn fat in the long term.
However, it’s important to note that the body also can use fat as an energy source, which occurs through a process known as beta-oxidation, which breaks down fatty acids to produce energy.
However, this process is less efficient than using glucose as a fuel source and requires more oxygen to produce the same amount of energy.
Without sufficient oxygen, such as during high-intensity exercise, the body may be unable to rely on fat as a primary energy source.
In addition to providing energy for fat-burning processes, carbohydrates also play a crucial role in providing energy for workouts and daily activities.
Carbohydrates are stored in the muscles and liver as glycogen, which can be quickly converted into glucose when energy is needed, making carbohydrates an important fuel source for high-intensity exercise and other activities requiring quick energy bursts.
Overall, carbohydrates play an important role in promoting overall health and supporting weight loss.
While it’s important to be mindful of carbohydrate intake and choose healthy sources of carbohydrates, such as whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, it’s equally important to ensure a sufficient intake to support energy levels and efficient fat-burning processes.
Fiber
Fiber is a type of carbohydrate not digested by the body, and it’s divided into two main categories: soluble and insoluble fiber.
Soluble fiber dissolves in water and forms a gel-like substance that helps slow digestion, while insoluble fiber does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, promoting regular bowel movements.
One of the main benefits of fiber is its role in regulating digestion and controlling blood sugar levels.
Soluble fiber helps slow down glucose absorption, reducing the likelihood of blood sugar spikes and crashes, which can lead to overeating and increased hunger.
By keeping blood sugar levels stable, fiber can also help promote feelings of fullness and satiety, reducing overall calorie intake.
In addition, fiber has a significant impact on gut health. The gut contains trillions of bacteria that play a crucial role in digestion, metabolism, and immune function.
A healthy gut microbiome is essential for overall health, and fiber is a key nutrient for promoting the growth of healthy gut bacteria.
By nourishing beneficial gut bacteria, fiber helps support immune function, improve nutrient absorption, and reduce the risk of certain diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
Although fiber cannot be digested by the body and, as such, passes through the digestive system mostly intact, it is not entirely useless.
Fiber can be fermented by the beneficial bacteria that reside in the gut, acting as a prebiotic.
Prebiotics are non-digestible food components that promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
These beneficial bacteria, also known as probiotics, help break down food and produce short-chain fatty acids, which provide energy for the body’s cells.
Fiber acts as a prebiotic by providing a food source for beneficial bacteria in the gut.
These bacteria can ferment the fiber and produce short-chain fatty acids, such as butyrate, acetate, and propionate.
These fatty acids provide energy for the cells lining the colon and play a vital role in maintaining colon health.
Research suggests that a diet high in fiber can help promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, leading to improved digestion, immune function, and overall health.
Additionally, some studies have shown that increased fiber intake can help with weight loss efforts by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake.
It’s important to consume a variety of fiber-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, nuts, and seeds.
Aim for at least 25-30 grams of fiber daily, and gradually increase your intake to prevent digestive discomfort.
It’s also essential to drink plenty of water when consuming fiber, as it absorbs water and can cause constipation if not enough water is consumed.
The book Fiber Fueled is an outstanding resource for more information on how a high-fiber diet can transform your health and body. It is one of the best books on nutrition education.
I read this book a couple of summers ago, and it made a huge impact on how I look at my food choices.
Dietary Fats
Dietary fats are often demonized as being unhealthy and contributing to weight gain.
However, this is not entirely accurate.
In fact, dietary fats play an essential role in promoting overall health and supporting weight loss goals.
One important role of dietary fats is their contribution to the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K).
Without dietary fats, these vitamins cannot be properly absorbed and utilized by the body.
In addition, dietary fats play a crucial role in hormone regulation.
Hormones such as testosterone, estrogen, and cortisol require dietary fats for production and regulation.
If you’re looking to lose weight fast for men, specific approaches tailored to male metabolism and fat loss can help achieve rapid but sustainable results due to the amount of testosterone men have and their muscle-building capabilities.
Moreover, dietary fats are essential for brain function and development.
The brain comprises approximately 60% fat, and dietary fats provide the building blocks for brain cells and neurotransmitters.
In terms of weight loss, consuming dietary fats can actually promote weight loss by increasing satiety and reducing overall calorie intake.
Fats take longer to digest and can help individuals feel full and satisfied for longer periods, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
Furthermore, certain types of dietary fats, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties and can improve heart health by reducing LDL (bad) cholesterol levels and increasing HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
It is important to note that not all fats are created equal.
Saturated and trans fats, often found in processed and fried foods, should be limited or avoided altogether.
Instead, individuals should focus on consuming healthy dietary fats like nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil, and fatty fish.
Overall, dietary fats play a crucial role in promoting overall health and supporting weight loss goals.
Consuming healthy sources of dietary fats in moderation can provide numerous health benefits and support healthy weight loss and management.
Hydration

Hydration plays an important role in healthy weight loss as it helps to regulate metabolism, suppress appetite, and increase energy levels.
For example, drinking water before meals can help to reduce appetite and promote weight loss.
Studies have shown that drinking water before meals can decrease calorie intake, as it helps to create a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
In addition to water, cold-pressed juices can be a good source of micronutrients, as they contain a high concentration of vitamins and minerals from fruits and vegetables.
However, it is important to note that cold-pressed juices can also contain a high amount of natural sugars and should be consumed in moderation.
Juicing once a day can promote weight loss by providing necessary micronutrients for your diet, but drinking too much juice, even natural, cold-pressed juice, can add unnecessary calories.
Beverages such as black coffee, green tea, oolong tea, and yerba mate tea can promote metabolism and increase fat burning.
These beverages contain caffeine, which can stimulate the central nervous system and increase energy expenditure.
Additionally, green tea and oolong tea contain compounds called catechins, which have been shown to increase metabolism and promote fat burning.
However, it is important to note that adding sugar or high-fat dairy products to coffee or tea can negate its potential weight loss benefits.
Poor beverage choices such as artificial juices, soda, and sugar-sweetened beverages can lead to weight gain, as they often contain high amounts of added sugars and empty calories.
These beverages provide little nutritional value and can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, leading to increased fat storage.
Good beverage choices for hydration include water, coconut water, herbal teas, and low-sugar sports drinks.
Coconut water is a good source of electrolytes and can help to replenish the body’s fluids after exercise.
Herbal teas, such as chamomile and peppermint, can also help to promote relaxation and reduce stress, which can aid in weight loss efforts.
Maintaining adequate hydration is relatively simple, and the most important key is drinking when thirsty.
If you choose one of the beverages listed above and drink when thirsty, you will likely remain well-hydrated.
Nourishing the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome refers to the trillions of microorganisms that reside in the gastrointestinal tract, including bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
These microorganisms play an essential role in digestion, metabolism, and overall health.
Recent research has also shown that the gut microbiome plays a crucial role in weight management, and nourishing it with prebiotic and probiotic foods and supplements can support healthy weight loss.
As mentioned before, prebiotics are non-digestible carbohydrates that serve as food for the beneficial bacteria in the gut.
Common sources of prebiotics include dietary fibers such as inulin, fructooligosaccharides (FOS), and galactooligosaccharides (GOS).
Prebiotics promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, which can improve gut health and aid in weight loss.
On the other hand, probiotics are live microorganisms that confer health benefits to the host when consumed in adequate amounts.
Probiotics can help restore the balance of gut bacteria, which can be disrupted by factors such as a poor diet, antibiotics, and stress. Some strains of probiotics have been shown to aid in weight loss.
Several mechanisms have been proposed to explain how prebiotics and probiotics can support healthy weight loss:
- Regulation of Appetite and Satiety: Prebiotics and probiotics can affect the levels of hormones such as ghrelin and leptin, which regulate appetite and satiety. Ghrelin stimulates appetite, while leptin suppresses appetite. Prebiotics and probiotics can increase leptin production and reduce the production of ghrelin, leading to reduced calorie intake and increased feelings of fullness.
- Regulation of Energy Metabolism: Prebiotics and probiotics can affect how the body uses energy, leading to increased calorie expenditure and fat burning. They can also improve insulin sensitivity, improving glucose uptake and reducing fat storage.
- Reduction of Inflammation: Chronic inflammation has been linked to obesity and metabolic disorders. Prebiotics and probiotics can reduce gut and body inflammation, leading to improved metabolic health.
Some prebiotic and probiotic foods that can aid in healthy weight loss include:
- Prebiotic Foods: Chicory root, Jerusalem artichokes, garlic, onions, leeks, asparagus, bananas, apples, oats, and barley.
- Probiotic Foods: Yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, kimchi, pickles, miso, tempeh, and kombucha.
In addition to consuming prebiotic and probiotic foods, supplements are also available in the form of capsules, tablets, and powders.
Although there are many useless supplements, the general consensus based on various research studies is that combining probiotic and prebiotic supplements can improve your gut microbiome’s health and help support healthy weight loss.
It is important to choose a reputable brand and consult with a healthcare professional before taking any supplements.

Best Supplements for Weight Loss
With so many options available, it can be challenging to navigate the world of supplements and determine which ones are effective and safe.
To simplify this process, let’s explore the science behind a few popular supplements for weight loss and determine whether they are worth considering.
CLA
CLA (Conjugated Linoleic Acid) is a fatty acid found in meat and dairy products, and it is thought to work by reducing the amount of fat stored in fat cells, increasing the breakdown of fat, and reducing appetite.
Studies have shown mixed results, with some indicating modest weight loss, while others have found no significant effects.
Overall, the evidence for CLA as a weight loss supplement is limited.
In my opinion, this is the best and most affordable CLA supplement:
Last update on 2025-07-13 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
L-Carnitine
L-carnitine is an amino acid that helps transport fatty acids into cells to be burned for energy, and it is often marketed as a fat burner and muscle builder.
Studies have shown that L-Carnitine can increase fat burning and reduce muscle soreness after exercise.
However, the effects on weight loss are relatively small, and more research is needed to determine its effectiveness.
I believe Dr. Martin’s Nutrition L-Carnitine is the best l-carnitine supplement to help you lose weight:
Last update on 2025-07-13 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Caffeine
Caffeine is a natural stimulant found in coffee, tea, and some supplements, and it works by increasing metabolism and fat burning and reducing appetite.
Studies have shown that caffeine can increase energy expenditure, leading to modest weight loss.
However, the effects may vary depending on the individual’s tolerance and sensitivity to caffeine.
There are a lot of caffeinated drinks that can help with weight loss, but currently, I suggest people drink Celsius drinks for weight loss since they contain caffeine, green tea extract, and other weight-loss-boosting ingredients.
Celsius drinks can help you burn fat by suppressing your appetite, stimulating your metabolism, and providing a healthy jolt of energy from caffeine.
Try the Celsius on-the-go packets for an affordable, eco-friendly option:
Last update on 2025-07-13 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Green Tea Extract
Green tea can promote weight loss for various reasons, and green tea extract is a popular supplement that can provide real benefits.
Green tea extract is a popular weight loss supplement with a high concentration of catechins, an antioxidant that boosts metabolism and fat burning.
Additionally, green tea extract may help reduce appetite, making it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet.
Studies have found that taking green tea extract can help to increase fat oxidation and energy expenditure, leading to greater weight loss over time.
However, it’s important to note that the effects of green tea extract may not be significant enough to produce weight loss on its own.
Green Coffee Bean Extract
Green coffee bean extract is a popular weight loss supplement with a high concentration of chlorogenic acid, a substance that has been shown to inhibit the absorption of carbohydrates and increase fat metabolism.
Additionally, green coffee bean extract may help reduce appetite and promote feelings of fullness, making it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet.
While studies have shown that green coffee bean extract can help promote weight loss, the effects are typically modest and may not be enough to produce significant weight loss.
Protein Powder Supplements
Protein powder supplements are a popular dietary supplement often used by athletes and fitness enthusiasts to support muscle growth and recovery, and they also have weight loss and fat-burning benefits.
Research has found that protein can help to reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness, making it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet.
Additionally, protein can also help to support muscle mass, which can increase metabolism and lead to greater fat-burning over time.
If you are interested in using a protein powder supplement, I suggest choosing a plant-based protein supplement.
Vegan protein powders may be better for weight loss than animal protein powders for several reasons:
- Lower in Calories: Plant protein powders, such as pea or hemp protein, are often lower in calories than animal protein powders. For example, a serving of pea protein powder typically contains around 100 calories, while a serving of whey protein powder can contain up to 150 calories.
- Higher in Fiber: Plant protein powders are often higher in fiber than animal protein powders, which can help you feel fuller for longer and reduce calorie intake. Fiber also plays a role in regulating blood sugar levels and supporting digestive health.
- More Sustainable: Plant protein powders are typically more sustainable and environmentally friendly than animal protein powders. Animal protein production requires more resources and generates more greenhouse gas emissions than plant protein production.
Overall, plant protein powders can be a great choice for individuals looking to lose weight or improve their overall health.
However, the most important point is to choose a high-quality plant protein powder that provides all the essential amino acids and is free from added sugars and artificial ingredients.
My favorite protein powder supplement is Garden of Life Protein and Greens.
Last update on 2025-07-13 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is a type of vinegar made from apples and is often used in cooking and as a natural remedy for various health conditions.
Some studies have suggested that apple cider vinegar may also have weight loss and fat-burning benefits.
Apple cider vinegar may help to reduce appetite and increase feelings of fullness, making it easier to stick to a calorie-controlled diet.
Additionally, apple cider vinegar may also help to increase fat metabolism, leading to greater weight loss over time.
However, it’s important to note that the effects of apple cider vinegar on weight loss and fat burning are limited and may not be enough to produce significant weight loss on its own.
Combining turmeric and ACV is a popular home remedy for weight loss.
Similarly, combining ACV and garcinia cambogia for weight loss is a common tactic, but I recommend skipping garcinia because there are safety concerns associated with garcinia cambogia supplementation.
Last update on 2025-07-13 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Turmeric
Turmeric is a spice that is commonly used in Indian cuisine and has been linked to a range of health benefits, including weight loss and fat burning.
It is believed that the active ingredient in turmeric, curcumin, can help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which can contribute to weight gain.
Additionally, animal studies have shown curcumin can increase metabolism and fat burning.
However, more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits of turmeric for weight loss in humans.
Step 3: Start an Exercise Routine

Regular exercise is a crucial component of weight loss and fat burning.
Exercise helps increase calorie expenditure, build muscle, and improve overall health.
There are two main types of exercise that can aid in weight loss and fat burning: cardio and resistance training.
Cardiovascular Exercise for Weight Loss
Cardiovascular exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, increase heart rate and calorie expenditure, leading to fat burning.
These activities are also excellent for improving cardiovascular health, endurance, and overall fitness.
Low-Intensity Steady State Cardio vs. High-Intensity Training for Weight Loss
Low-intensity steady-state (LISS) cardio and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) are two popular cardio workouts for weight loss and fat burning.
LISS cardio involves exercising at a moderate intensity level for an extended period, typically 30 to 60 minutes.
Examples include walking, jogging, or cycling at a steady pace.
LISS cardio is relatively low-impact and is ideal for beginners or individuals with joint issues.
On the other hand, HIIT involves short bursts of high-intensity exercise followed by brief rest periods.
HIIT can be more intense than LISS cardio and can lead to increased calorie burn during and after the exercise session. HIIT can include activities like sprinting, jumping jacks, or burpees.
Due to its higher intensity and afterburn effect, research suggests that HIIT can be more effective for fat loss and calorie burning than LISS cardio.
However, some people may argue that low-intensity exercise is better for weight loss and fat burning because there is a target heart rate zone for predominately burning body fat.
The “fat-burning heart rate zone” is a target heart rate range often recommended for people who want to burn fat during exercise, and it is believed that exercising at this heart rate zone will primarily use fat as a fuel source, as opposed to carbohydrates.
The heart rate range is typically calculated as 60-70% of an individual’s maximum heart rate.
While exercising in the fat-burning heart rate zone can lead to burning fat during exercise, it is not necessarily the most effective way to lose weight or burn fat.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) or other forms of high-intensity exercise can be more effective at burning calories both during and after exercise because high-intensity exercise can increase the body’s metabolic rate, leading to more calorie burning even at rest.
Confusion about choosing low-intensity steady state (LISS) or high-intensity exercise for weight loss can arise because people may hear conflicting information about which is better for fat burning.
While it is true that exercising at a lower intensity may burn a higher percentage of fat during the exercise session, it may not lead to as many overall calories burned as in high-intensity exercise.
Therefore, HIIT or other forms of high-intensity exercise may be more effective for weight loss and fat burning in the long run.
However, both LISS cardio and HIIT have their benefits, and incorporating both into a fitness routine can lead to optimal results.
LISS cardio can help build endurance and burn calories during the exercise session, while HIIT can provide a metabolic boost and lead to increased calorie burn after the workout.
Ultimately, the best form of exercise for weight loss and fat burning depends on an individual’s fitness level, preferences, and goals.
A mix of LISS cardio and HIIT can help individuals achieve a well-rounded fitness routine and promote weight loss and fat burning.
Resistance Training
Resistance training (also known as strength training) is an essential component of any weight loss program.
Strength training involves lifting weights, using resistance bands, or performing bodyweight exercises like push-ups, squats, and lunges, and it can increase muscle mass and strength.
Building muscle is important because muscle is metabolically active tissue that burns calories even at rest.
The more muscle mass a person has, the higher their resting metabolic rate, which means they burn more calories throughout the day.
Resistance training has been shown to increase muscle mass and, therefore, increase resting metabolic rate, leading to increased fat burning and weight loss.
Furthermore, resistance training is important for preventing metabolic adaptations to weight loss because it helps to preserve lean body mass.
When someone loses weight, they tend to lose both fat and muscle mass, which can lead to a decrease in resting metabolic rate (RMR).
When an individual engages in resistance training, they stimulate muscle protein synthesis, which helps to preserve and even increase muscle mass.
This increase in lean body mass from resistance training can help prevent the decrease in RMR that often occurs with weight loss.
Additionally, resistance training can help to improve insulin sensitivity, which is the ability of your cells to respond to insulin and use glucose for energy.
Improved insulin sensitivity can help to prevent the metabolic adaptations that can occur with weight loss, such as a decrease in energy expenditure and an increase in hunger.
In addition to increasing metabolism and promoting fat burning, resistance training can improve bone density, reduce the risk of injury, and improve overall physical function.
When it comes to resistance training, it’s important to focus on all major muscle groups.
This includes exercises such as squats, lunges, push-ups, pull-ups, and deadlifts.
It’s also important to gradually increase the weight or resistance used during these exercises over time to continue challenging the muscles and promote muscle growth.
As with cardio workouts, the frequency, duration, and intensity of resistance training can vary depending on an individual’s fitness level, health status, and goals.
However, it is generally recommended to aim for two to three sessions per week, with at least one day of rest in between sessions.
The American College of Sports Medicine recommends that adults engage in resistance training exercises at least twice weekly, targeting all major muscle groups.
When starting a resistance training program, it’s important to start gradually and progress slowly over time.
Beginners can start with lighter weights and fewer sets and gradually increase the intensity and duration of the workout as they become stronger and more confident.
Combining resistance training with cardiovascular exercise is ideal for weight loss and overall health.
NEAT (Non-exercise Activity Thermogenesis)
As I mentioned earlier in the article, Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis (NEAT) refers to the energy expended through daily activities that are not considered exercise.
These activities can increase calorie expenditure and promote weight loss.
Forms of NEAT include walking or biking to work, taking the stairs instead of the elevator, standing at your desk, and even fidgeting while sitting.
Walking is a great form of exercise for weight loss, and counting steps is a valuable way to track daily NEAT.
Any activity that requires movement and increases energy expenditure beyond resting metabolic rate can be considered NEAT.
While NEAT may not burn as many calories as formal exercise, the cumulative effect of these small daily activities can add up to a significant amount of calories burned.
In fact, studies have shown that NEAT can account for up to 50% of an individual’s daily calorie expenditure.
Incorporating more NEAT into daily life can effectively increase calorie expenditure and support weight loss efforts.
Some strategies for increasing NEAT include:
- Walking or biking to work
- Taking the stairs instead of the elevator
- Standing at your desk or during meetings
- Fidgeting while sitting
- Doing household chores, such as vacuuming or gardening
- Parking farther away from the entrance to a building
- Taking frequent breaks from sitting to stand and move around
Step 4: Make These Lifestyle Changes for Weight Loss
In addition to exercise, lifestyle changes can also play an important role in weight loss and fat burning.
Sleep 7-8 Hours Per Night
Sleep and fitness go hand in hand, as getting adequate sleep is crucial because lack of sleep can disrupt the hormones that regulate appetite and metabolism, leading to increased calorie intake and reduced calorie expenditure.
Aim for at least 7-8 hours of sleep per night to promote weight loss.
Focus on Managing Stress
Stress is another factor that can lead to weight gain and hinder weight loss efforts.
Chronic stress can increase the hormone cortisol, which is associated with increased appetite and fat storage.
Cortisol is often referred to as the “stress hormone” because it is released in response to physical and emotional stress.
Cortisol stimulates the release of glucose from the liver, which increases blood sugar levels and provides energy to the body.
In the short term, cortisol can provide the body with the energy it needs to deal with stress.
However, elevated cortisol levels for extended periods can lead to increased fat retention, particularly in the abdominal region.
Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood sugar levels.
When we eat, insulin is released by the pancreas to help the body use glucose for energy or store it for later use. Insulin resistance occurs when the body becomes less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels and increased fat storage.
Ghrelin is a hormone that stimulates appetite and increases food intake.
Ghrelin is released when the stomach is empty and signals the brain to increase hunger and seek out food.
Ghrelin levels can also increase in response to stress, leading to overeating and weight gain.
Going for a walk outside, mindful meditation, progressive muscle relaxation, and targeted breathwork are a few of my favorite natural remedies for stress relief.
If you have never done targeted breathing exercises, I suggest the Breathwrk App. I have been using BreathWrk for nearly two years, and it is a consistent part of my daily routine.
In addition, mindfulness and stress management can help regulate insulin levels by promoting healthy eating habits and reducing overeating.
Finally, these techniques can help regulate ghrelin levels by promoting mindful eating and reducing stress-induced overeating.
By reducing stress and regulating these hormones, mindfulness and stress management techniques can support weight loss efforts.
Stop Smoking or Drinking Alcohol
Unhealthy habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can also hinder weight loss and fat burning.
Smoking can reduce metabolism and increase appetite, while excessive alcohol consumption can lead to increased calorie intake and reduced calorie expenditure.
Making positive lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking and stopping to consume alcohol can play a huge role in long-term weight loss success.
Step 5: Track Your Progress and Stay Motivated
Losing weight and burning fat can be a challenging journey, but tracking progress is an essential tool to help keep you motivated and on track.
By monitoring your body weight and body fat percentage and taking measurements, you can see how far you’ve come and celebrate your progress.
Additionally, it’s important to set realistic goals and not get discouraged if you hit a plateau.
Remind yourself why you started and seek support from friends and family when needed.
To achieve long-term weight loss and weight-maintenance success, it’s important to take a multifaceted approach that combines diet, exercise, lifestyle changes, and supplementation.
You need to create a calorie deficit through a healthy diet and exercise routine, consume a balanced diet that is high in protein, fiber, and healthy fats, engage in both cardio and resistance training, and adopt healthy habits such as getting enough sleep and managing stress properly.
While supplements can aid in weight loss and fat burning, they should not be relied upon as the sole means of weight loss.
In conclusion, remember that weight loss is a journey, and there is no quick fix.
Even if progress feels slow at first, trust that small changes to lose weight, when repeated consistently, can transform your body, mindset, and overall health in ways that last a lifetime.
Seeing results takes time, effort, and dedication, but it’s worth it for your health and well-being.
Don’t forget to track your progress, set realistic goals, seek support, and take a multifaceted approach to achieve your goals.
With the right mindset and knowledge, you can achieve and maintain your desired weight and body composition.
For a quick reset to your overall health, sign up for my email newsletter and receive my free 7-Day Detox plan, which walks you through a full week of clean eating, mindful movement, and lifestyle changes that work.
Subscribe to My Newsletter

Subscribe to my newsletter to receive occasional updates on new articles and health and fitness tips. Also, you will receive my 60-page eBook on resetting your body and mind in 7 days for FREE!
Read Next: Weight Loss for Dummies
This website does not provide medical advice. This website site does contain affiliate links, and purchases may earn a commission.
Read my Medical Disclaimer, Review Disclaimer, and Publishing Policies for more details. Use of this site indicates acceptance of these terms.







