The Ketogenic Diet for Athletes: Everything You Need to Know
Many people have heard about the Ketogenic Diet, but did you know it is a viable solution for athletes as well?
This high-fat, low-carb diet shifts the body into a metabolic state called ketosis.
But what’s intriguing is its potential beyond weight loss: Can this diet revolutionize athletic performance as well?
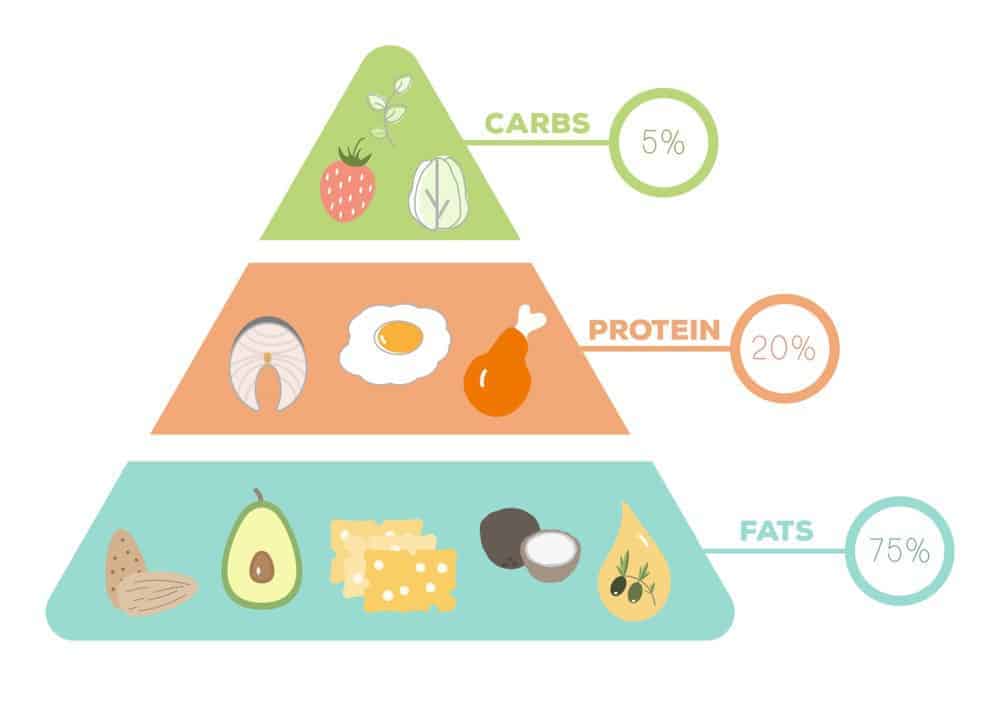
At the heart of the Ketogenic Diet is a dramatic reduction in carbohydrate intake, coupled with a significant increase in protein and healthy fats.
It’s not just about what you eat but also when, as the diet aligns closely with intermittent fasting principles, advocating for skipping breakfast at times.
Hydration and balanced salt intake are also key components.
While the diet has surged in popularity recently, its effectiveness extends beyond the scale.
Studies suggest that a very low-carb Ketogenic Diet can preserve muscle mass and strength, even during rapid weight loss (Casanueva et al., 2020).
However, it’s not without its challenges, especially for athletes.
A study in the Open Access Journal of Sports Medicine reveals a mixed bag: athletes on a Ketogenic Diet don’t experience reduced performance in moderate-to-vigorous exercises.
Yet, at higher intensity levels (>70% VO2max), a decrease in exercise economy might hinder performance in real-world scenarios.
This poses a dilemma: can athletes on a ketogenic diet maintain muscle gains and peak performance while operating on minimal carbs?
Navigating this diet as an athlete seems daunting, yet it’s achievable.
The key lies in understanding how to fuel high-intensity workouts within the diet’s constraints.
This approach not only offers a path to an aesthetic physique but also preserves athletic functionality.
Keep reading below to find out how to use the ketogenic diet as an athlete.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet for Athletes
The Ketogenic Diet, characterized by its low carbohydrate and high fat intake, offers several potential benefits for athletes, a topic that’s gaining traction in sports nutrition circles.
Here’s a closer look at the benefits of the ketogenic diet for athletes:
- Enhanced Fat Oxidation and Energy Efficiency: One of the most significant advantages of the Ketogenic Diet is the increased reliance on fat as an energy source. This shift can enhance fat oxidation, which is crucial for endurance athletes who participate in prolonged activities (Volek et al., 2015). By utilizing fat stores for energy, athletes can potentially improve their endurance and performance in long-duration events.
- Weight and Body Composition Management: Athletes often seek to optimize body composition for performance and aesthetic purposes. The Ketogenic Diet has been shown to aid in reducing body fat while preserving lean muscle mass (Paoli et al., 2012), making it an attractive option for weight-class athletes or those looking to improve their power-to-weight ratio.
- Reduced Dependence on Carbohydrate Loading: Traditional sports nutrition often emphasizes carbohydrate loading to maximize glycogen stores. However, athletes on a Ketogenic Diet become adapted to using fats as their primary energy source, reducing their dependence on carbohydrates for energy and potentially avoiding issues related to glycogen depletion.
- Stable Blood Glucose Levels: For athletes, particularly those with conditions like diabetes, maintaining stable blood glucose levels is critical. The Ketogenic Diet can offer more stable blood glucose levels, reducing the risks of both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia during prolonged physical activity (McSwiney et al., 2018).
- Reduced Inflammation and Improved Recovery: Some research suggests that a Ketogenic Diet may help reduce inflammation, a key factor in recovery and performance. Lower inflammation can result in quicker recovery times and less post-exercise soreness.
- Cognitive and Mental Health Benefits: Aside from physical benefits, the Ketogenic Diet may also offer cognitive advantages. This aspect is particularly important in sports, where focus and mental clarity are as crucial as physical ability (Murray & Rosenbloom, 2018).
- Appetite Control: The high fat and moderate protein intake associated with the Ketogenic Diet can lead to a greater feeling of fullness and reduced appetite, which can be beneficial for athletes managing their weight and dietary intake (Gibson et al., 2015).
The Ketogenic Diet presents a range of potential benefits for athletes, from enhanced energy efficiency and weight management to improved recovery and mental clarity.
However, it’s essential to note that individual responses can vary, and athletes should consult with nutrition professionals to tailor the diet to their specific needs and goals.
Negatives of Keto for Athletes
While the Ketogenic Diet offers unique benefits for athletes, it’s crucial to consider its potential drawbacks, especially regarding carbohydrate restriction and lifestyle suitability.
Athletes can use a ketogenic diet for several benefits, including rapid, short-term weight loss and improved insulin resistance.
However, there are negative aspects of the ketogenic diets for athletes, such as the difficulty of long-term maintenance and increased triglyceride levels (Mooradian, 2020).
The Role of Carbohydrates in Athletic Performance: Carbohydrates are not just a crucial energy source; they’re the body’s preferred fuel, particularly for high-intensity activities. They’re swiftly converted into glucose, powering everything from brain function to daily physical tasks. Beyond energy, carbohydrates in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are packed with essential micronutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals. Athletes on a Ketogenic Diet might miss out on these valuable components, affecting both their energy efficiency and nutritional balance.
Lifestyle Compatibility and Diet Sustainability: Another aspect to consider is how well the Ketogenic Diet fits into an athlete’s lifestyle. For most people, diets like the Mediterranean Diet, known for its balance and sustainability over time, might be more practical. This diet has been shown to aid in weight loss, improve glucose control, and promote overall health, and is often seen as more sustainable long-term (Bolla et al., 2019).
Assessing Goals and Activity Levels: If you’re an athlete contemplating the Ketogenic Diet, reflect on your objectives. For rapid, short-term weight loss, a slightly lower carbohydrate intake, around 40-50% of your total daily nutrients (just below the Acceptable Macronutrient Distribution Range [AMDR] of 45-65%), could be effective. This approach might suit those with a sedentary lifestyle better. In contrast, highly active individuals or those engaged in intense physical training may benefit more from a higher carbohydrate intake, aligning with the upper end of the AMDR. This is because as physical activity intensifies, the body increasingly relies on carbohydrates as its primary energy source.
While the Ketogenic Diet can be a valuable tool for athletes, it’s not a one-size-fits-all solution. The decision to adopt this diet should be made with careful consideration of one’s individual goals, lifestyle, and the specific demands of their athletic endeavors.
Is the Ketogenic Diet Safe for Athletes?
The safety of the Ketogenic Diet for athletes sparks intriguing discussions, especially when considering unique cases like that of a 37-year-old cyclist with Type 1 Diabetes (Nolan et al., 2019).
This individual’s journey offers a unique lens into the diet’s implications for athletes managing chronic conditions.
Type 1 Diabetes, characterized by the body’s inability to produce sufficient insulin, necessitates careful monitoring of glucose intake.
For four years leading up to his ambitious 4011km bike ride over 20 days, the cyclist adhered to a strict, very-low-carbohydrate Ketogenic Diet, limiting his daily carb intake to 25-30 grams.
The ride, featuring days with over 250 km of cycling and no rest days, was a true test of endurance and dietary management.
Notably, the cyclist experienced just one hypoglycemic episode, swiftly managed by carbohydrate intake.
His blood glucose levels remained remarkably stable, with an average deviation of only 2.1 mmol/l and minimal time spent above the ten mmol/l threshold.
While this case underscores the potential of a Ketogenic Diet in managing blood sugar levels for active individuals, broader and more controlled research is crucial for a comprehensive understanding.
The effects on glycemic variability in active populations, and how quickly these benefits manifest, remain areas ripe for exploration.
The broader narrative around high-protein, low-carb diets is equally revealing.
A study in Nutrition Reviews highlights how dietary protein influences energy intake through satiety and increases energy expenditure via the thermic effect of feeding.
While fixed energy intake, studies showed limited impact on weight and fat loss; one ad libitum study suggested that high-protein diets could lead to more substantial reductions in energy and fat intake.
Moreover, research in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition (2008) found that in the short term, high-protein, low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets significantly reduce hunger and food intake more than high-protein, medium-carbohydrate nonketogenic diets.
This aspect is particularly relevant for athletes who need to manage their weight and body composition without compromising on energy and nutritional needs.
To sum up, while the Ketogenic Diet shows promise for athletes, especially in terms of blood sugar management and weight control, its full implications for athletic performance, particularly in high-intensity scenarios, require further exploration.
Athletes considering this diet should do so under professional guidance, ensuring it aligns with their individual health needs and performance goals.
How Athletes Can Get into Ketosis Safely
Transitioning into ketosis, where the body burns fat for fuel, requires careful consideration, especially for athletes.
In ketosis, your body produces ketones from fatty acids and acetyl CoA (acetyl coenzyme A), which become your primary energy source.
This metabolic shift is at the heart of the Ketogenic Diet’s effectiveness.
While ketosis can utilize body fat effectively, it’s crucial to balance this with maintaining lean muscle mass and overall health.
Below are strategic steps to help athletes enter ketosis safely and sustainably:
Gradual Reduction of Carbohydrate Intake
The cornerstone of reaching ketosis is significantly lowering carbohydrate consumption.
Normally, your body uses glucose, stored as glycogen in muscles and the liver, as its primary energy source.
By reducing your daily carb intake, you deplete these glycogen stores, prompting your body to seek alternative energy sources.
Aim to limit carbs to a maximum of 50 grams per day, but do it gradually to avoid shocking your system.
Increase Protein and Healthy Fats
As you cut down on carbs, it’s vital to compensate with healthy fats and proteins.
This not only provides essential nutrition but also helps with satiety and maintains muscle mass.
A study in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition highlights that high-protein diets increase satiety and thermogenesis and help in maintaining or building fat-free mass.
However, it’s important to choose your protein sources wisely.
While animal proteins are common in low-carb diets, they often come with high levels of saturated fats, especially red meat, which is linked to heart disease risks.
Instead, focus on lean protein sources and unsaturated fats, like those found in fish such as salmon.
Monitor Nutrient Intake for Balanced Diet
Entering ketosis shouldn’t mean compromising on essential nutrients.
Pay attention to your intake of vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients, often found in carbohydrate-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Supplementing your diet or carefully selecting low-carb but nutrient-dense foods can help mitigate this issue.
How to Exercise When You’re In Ketosis
Achieving ketosis as an athlete involves more than just following a diet; it’s about making informed, gradual changes to your eating habits while ensuring that your body receives the nutrients it needs for optimal performance and health.
Athletes on the Ketogenic Diet face unique challenges and opportunities when it comes to exercise.
Understanding how to adapt workout routines and carbohydrate intake is key to maximizing benefits while in ketosis.
1. Adjusting Exercise Routines: Initially, athletes might need to modify their exercise intensity and duration as the body adapts to burning fat for fuel. This transition period varies but usually lasts a few weeks. During this time, focus on steady, moderate-intensity workouts rather than high-intensity intervals to allow your body to adjust efficiently.
2. Exercise Benefits in Ketosis: Exercising in a state of ketosis can lead to enhanced fat burning and maintaining muscle mass. As the body becomes more efficient at utilizing fat for energy, athletes may notice improved endurance and stamina.
3. The Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD) for Athletes: For athletes who engage in regular, moderate exercise, the TKD approach can be effective. This involves consuming 25-50 grams of carbohydrates about 30-60 minutes before a workout. This strategy provides a temporary glucose boost for energy without significantly disrupting ketosis. Opt for easily digestible carbs like fruits or energy gels for this pre-workout intake.
4. The Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD) for High-Intensity Athletes: Athletes involved in high-intensity, frequent training may benefit from the CKD. This involves 1-2 days of higher carbohydrate intake (refeeding days) each week to replenish glycogen stores. It’s a strategic approach to balance the benefits of ketosis with the energy demands of intense workouts. During refeeding days, prioritize complex carbohydrates from whole foods like sweet potatoes, quinoa, or whole grains.
5. Transitioning Back to Ketosis: Post-refeeding, ease back into ketosis with a day of fasting or very low carbohydrate intake, followed by a day of moderate-intensity exercise before resuming the standard ketogenic diet. This cycle helps the body efficiently shift back into ketosis while maintaining energy levels for training.
6. Monitoring and Adjusting: It’s important for athletes to monitor their performance and recovery closely. Adjustments to diet and exercise may be necessary based on individual responses. Consulting with a sports nutritionist can provide personalized guidance.
By tailoring the ketogenic approach to their training needs, athletes can maintain peak performance while reaping the benefits of a fat-adapted metabolic state.
This requires a careful balance of nutrition and exercise strategies, but with the right approach, athletes can optimize their training and health on the Ketogenic Diet.
The Best Keto-Friendly Foods for Athletes
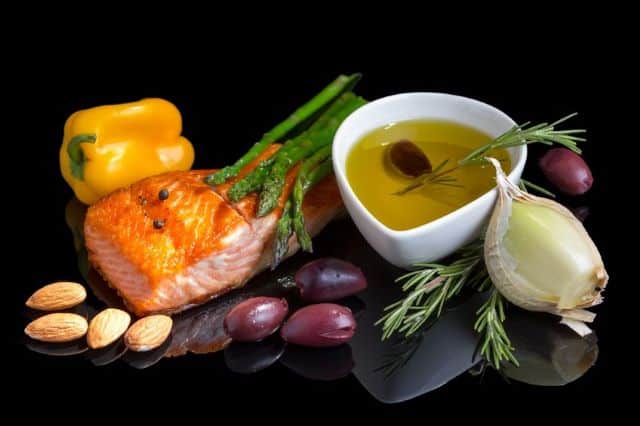

For athletes embracing the Ketogenic Diet, selecting the right foods is crucial for both performance and health.
Here’s an guide to keto-friendly foods that provide the necessary nutrients without compromising ketosis.
1. Seafood: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals, seafood is an excellent choice for athletes. Furthermore, as asserted by Eco Watch, all species of freshwater fish and marine water fish do not have any carb content. Fish like salmon and mackerel are virtually carb-free and packed with healthy fats and protein, supporting muscle recovery and reducing inflammation. Shellfish, while slightly higher in carbs, can still fit into a keto plan.
2. Low-Carb Vegetables: Vegetables like spinach and kale, broccoli, and cauliflower are low in carbs but high in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants. They’re essential for a balanced keto diet, providing nutrients often lacking in high-fat foods. These vegetables can be great substitutes for high-carb sides — think cauliflower rice or zucchini noodles.
3. Olives and Olive Oil: Olives are low in carbs and high in antioxidants, particularly oleuropein, which has been linked to blood pressure reduction. Olive oil, a staple in healthy diets, is rich in monounsaturated fats, beneficial for heart health and inflammation control.
4. Cheese: With minimal carbs and high fat, cheese is a great addition to the keto diet. It’s also a good source of protein and calcium. Cheese also contains conjugated linoleic acid, a nutrient that plays a role in optimizing body composition. However, moderation is key due to its saturated fat content. Opt for varieties like feta, mozzarella, and cheddar.
5. Avocados: Avocados are a keto superfood, offering fiber, potassium, and essential vitamins, along with healthy fats. They’re versatile and can be added to salads, smoothies, or eaten as a snack.
6. Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds are excellent for keto diets. They’re high in fats and fiber and moderate in protein, making them ideal for snacking or adding to meals. They also offer protective benefits against heart disease and inflammation. You can read more about low-carb nuts and seeds here.
7. Poultry and Meat: Lean meats and poultry are core components of the keto diet, providing high-quality protein and essential nutrients like zinc and selenium. Opt for grass-fed meats when possible for higher omega-3 content.
8. MCT Oil: What is MCT oil, you ask? MCT stands for Medium Chain Triglycerides, which are comprised of medium-chain fatty acids. MCT oil, derived from coconut oil, is a unique fat that’s efficiently converted to ketones by the body. It’s easily digestible and can be a quick energy source, making it ideal for adding to coffee or shakes. The benefits of MCT Oil and Coconut Oil are both impressive, and you can freely use whichever you desire if you are on the ketogenic diet. The website KetoaHolics can help you determine the best MCT Oil available.
Incorporating these foods into a ketogenic diet can help athletes maintain energy levels, muscle mass, and overall health while adhering to the diet’s low-carb, high-fat principles.
The Best Keto Supplements for Athletes
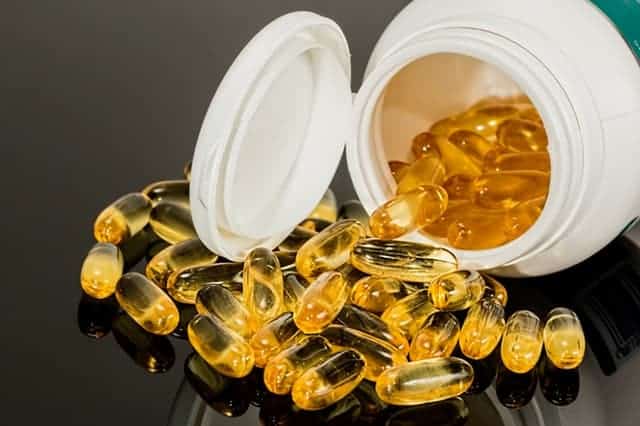

For athletes following a ketogenic diet, certain supplements can help optimize performance and health.
Taking advantage of the benefits of keto supplements can help you have more success with the keto diet and get better results.
Here’s a guide to some of the best keto supplements for athletes, focusing on efficacy and safety.
1. Omega-3 Fatty Acids (Fish Oil): Omega-3s are crucial for athletes, particularly those on a keto diet, due to their anti-inflammatory properties and benefits for heart and brain health. While there are concerns about the quality and oxidation of some fish oil supplements, choosing high-quality, third-party-tested products can mitigate these risks. Look for supplements with a high concentration of EPA and DHA and those certified for purity and sustainability.
2. MCT Oil: Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) are a popular supplement in the keto community. They are rapidly absorbed and converted into ketones, providing a quick energy source. MCT oil can be added to coffee, shakes, or salads. Quality matters here, too, so opt for a reputable brand that uses pure, non-GMO sources.
3. Electrolytes: The ketogenic diet can alter fluid and mineral balance. Supplementing with electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium can prevent imbalances that may affect performance, such as muscle cramps or fatigue. Electrolyte supplements specifically formulated for keto dieters can be particularly beneficial.
4. Vitamin D and Calcium: Vitamin D and calcium are essential for bone health, a critical consideration for athletes. Keto dieters might not get enough from their restricted diet, especially if dairy intake is limited. Supplements for bone health can help fill this gap.
5. Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): BCAAs can be beneficial for muscle recovery and growth. They may be particularly important on a keto diet to help preserve muscle mass, especially for athletes engaged in high-intensity or endurance training. Buying a BCAA or EAA supplement is one of the best choices for athletes using the ketogenic diet.
6. Collagen: Collagen supplements can support joint health and skin elasticity. For those on a ketogenic diet, collagen peptides are a great option as they are low in carbs and can be easily added to various foods and drinks.
7. Greens Powder: To ensure you’re getting a full spectrum of nutrients, including antioxidants and phytonutrients, a high-quality greens powder can be beneficial. It can compensate for the lower intake of certain fruits and vegetables on a keto diet. Bloom Greens & Superfoods is a good option here.
Concluding Thoughts – Is the Ketogenic Diet Good for Athletes?

Although it might seem difficult to control your diet, making the Ketogenic Switch can improve your health and maintain your performance as an athlete.
The Ketogenic Diet, characterized by low carbohydrate and high fat intake, presents both potential benefits and challenges for athletes.
Understanding these aspects is crucial in determining whether this diet aligns with an athlete’s goals and lifestyle.
1. Potential Benefits for Athletes: The diet has shown promise in aiding rapid weight loss and improving insulin sensitivity, which can be advantageous for certain athletic goals. It can also lead to enhanced fat burning, which might benefit endurance athletes. Moreover, some athletes report improved focus and mental clarity while in ketosis.
2. Challenges and Considerations: The diet’s restrictive nature poses challenges in long-term adherence. Concerns include the risk of nutrient deficiencies due to limited food variety and potential increases in triglyceride levels. Athletes, particularly those in high-intensity sports, may experience decreased performance during the adaptation phase and potentially longer-term due to reduced glycogen stores.
3. The Role of Carbohydrates in Athletic Performance: Carbohydrates are a primary fuel source, especially for high-intensity activities. They are crucial for overall energy levels and replenishing glycogen stores post-exercise. A complete exclusion of carbohydrates can lead to fatigue and reduced exercise capacity.
4. A Balanced Approach to Diet: Rather than strictly adhering to a low-carb regime, a moderately low-carb diet that emphasizes nutrient-dense sources like fruits and vegetables might be more sustainable and effective. This approach can help in maintaining a healthy calorie deficit for weight management without compromising energy and nutrient intake.
5. Personalization and Moderation: Each athlete’s dietary needs are unique, based on factors like the type of sport, training intensity, and individual metabolic responses. A personalized approach, possibly starting with a moderate reduction in carbohydrates and focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, is advisable. Consulting with a sports nutritionist can help tailor a diet plan to an athlete’s specific needs and goals.
While the Ketogenic Diet can offer certain advantages for athletes, its suitability depends on individual circumstances, the type of sport, and personal health goals.
Whether you are going to pack a keto lunch for work each day on your cyclical Keto Diet or maintain a rigorous targeted Keto Diet, adding the Ketogenic Diet to your life is an effective way for athletes to improve their health and body composition when done properly.
However, it’s essential to weigh its benefits against potential downsides, considering the critical role of carbohydrates in athletic performance and overall health.
Carbohydrates provide the necessary fuel for your entire body, and they provide many valuable nutrients that you cannot get from other foods.
If you would like to try restricting your carbohydrate intake to lose weight, you should first remember that the essence of weight loss is calories in vs calories out.
Regardless of how many carbohydrates you are consuming, if you are in a calorie deficit each day (consuming fewer calories than you are burning), you will lose weight.
Therefore, your goal, if you are trying to lose weight or improve your body composition, should be to find the type of diet you can maintain that allows you to have a healthy calorie deficit day after day.
Instead of focusing on keeping a very low-carb Ketogenic Diet, I would first suggest using a moderately-low carb diet (around 40-50% AMDR of carbohydrates per day), while choosing nutrient-dense carbohydrates.
I don’t suggest a low-carb Keto Diet for athletes mainly because it is difficult to fit into your lifestyle, and it is likely that you will feel depleted and tired.
A well-balanced diet that consists of a wide variety of whole, unprocessed plant foods, healthy fats, and lean protein that provides plenty of nutrients and helps athletes stay in a small yet significant calorie deficit per day is the healthiest dietary approach to long-term body composition improvements.
If an athlete is particularly worried about carbohydrate intake, I would additionally address the significance of reducing highly processed carbohydrates and added sugar consumption and replacing these foods with whole, unprocessed carbohydrate sources such as fruits and vegetables.
However, through the right type of food choices and proper carbohydrate consumption and timing, you’ll be able to reach your goals for both overall health and athletic performance with the Ketogenic Diet for athletes.
This website does not provide medical advice. This website site does contain affiliate links, and purchases may earn a commission.
Read my Medical Disclaimer, Review Disclaimer, and Publishing Policies for more details. Use of this site indicates acceptance of these terms.



