Analyzing the Best Cardio Alternatives to Running
When evaluating alternatives to running, it helps to step back and understand what cardiovascular training is actually meant to…
A well-rounded fitness plan isn’t just about lifting heavy weights or running long distances.
True physical development and long-term health come from integrating different types of exercise that work together to improve strength, endurance, mobility, coordination, and recovery.
Whether your goal is athletic performance, functional strength, or general wellness, understanding how to use each type of exercise or training modality can provide substantial benefits.
Below is a breakdown of the most important types of exercise, including subcategories and specific training tools that improve results.
Use the links to explore detailed guides on each one and learn how to build a workout program that supports total-body fitness.
Resistance training (also known as strength training) is the foundation of building lean muscle mass, increasing bone density, and improving metabolic health.
It involves working against a force, whether gravity, weights, or resistance bands, to build muscular strength and endurance.
Bodyweight exercises don’t require any additional resistance and can be done nearly anywhere.
Movements like push-ups, pull-ups, lunges, and planks build strength and coordination using your body as the resistance.
Dumbbells allow for versatile, unilateral training that improves balance, core engagement, and joint stability, whether you are a beginner or an advanced lifter looking to build functional strength.
Barbell training is ideal for developing maximal strength and power. Compound lifts such as squats, deadlifts, and bench presses engage multiple muscle groups and are staples for athletes and serious lifters.
Kettlebells offer a unique combination of strength and cardio. Some of the best kettlebell exercises include kettlebell swings, KB Turkish get-ups, KB goblet squats, and kettlebell snatches, which train explosive power, grip strength, and coordination, making them ideal for functional fitness.
Cardiovascular exercise (also known as aerobic exercise) supports heart health, lung capacity, and fat metabolism. It’s also essential for endurance, energy regulation, and overall longevity.
Common modalities include running, cycling, rowing, swimming, and jump rope.
To maximize results, you can train steady-state (LISS) or use interval-based approaches like High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT).
For fat-burning, cardio workouts for weight loss are most effective when combined with strength training and proper nutrition.
Plyometrics are explosive, high-intensity movements that train power, speed, and neuromuscular coordination.
Plyometric exercises like box jumps, jump squats, and depth drops develop fast-twitch muscle fibers and improve athleticism.
These are best used sparingly to prevent overuse injuries and are particularly valuable for athletes who need quick force production.

When evaluating alternatives to running, it helps to step back and understand what cardiovascular training is actually meant to…
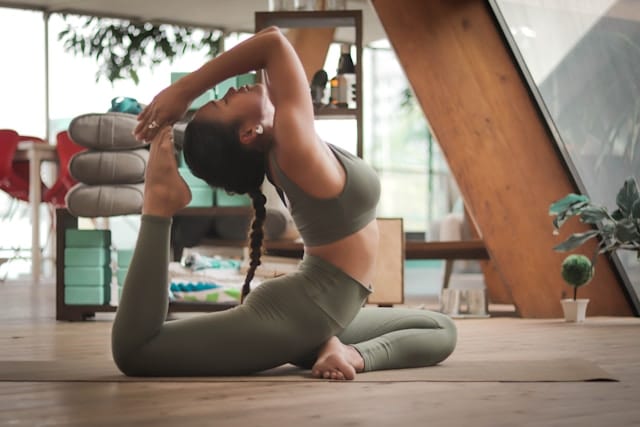

Fun ways to exercise are often the most effective approach for improving health because they increase consistency, enjoyment,…
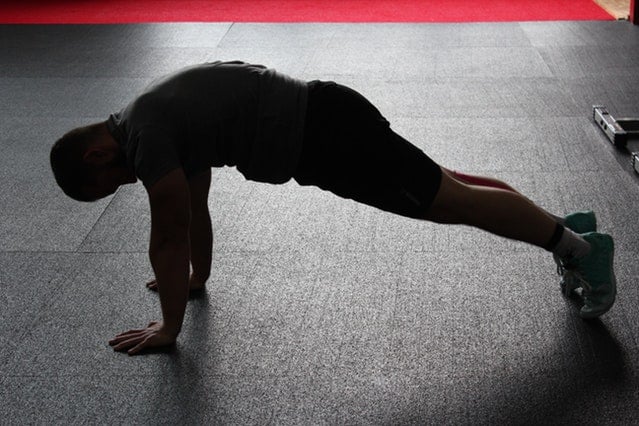

The best bodyweight exercises for beginners offer a simple, effective way to build strength, mobility, and confidence without needing…

Achieving strong, athletic legs starts with understanding the best bodyweight leg exercises, many of which build real-world strength without…
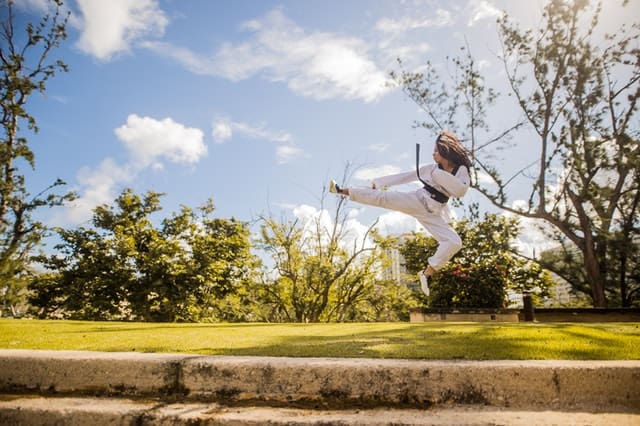

From improving cardiovascular health to boosting mental focus, the health benefits of martial arts extend to nearly every…
End of content
End of content

Want a free eBook?
Subscribe to my newsletter for occasional updates and receive my 60+ page eBook for free!

Want a free eBook?
Subscribe to my newsletter for occasional updates and receive my 60+ page eBook for free!